Difference between revisions of "Research"
(Created page with "== ABC-transporters == frame|right|Maltose transporter from ''E. coli'' Many essential functions of living cells are performed by nanoscale motors consisti...") |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
resistance of tumor cells after cancer patients receive chemotherapy. In bacterial cells, | resistance of tumor cells after cancer patients receive chemotherapy. In bacterial cells, | ||
ABC-transporters are responsible for extrusions of various antibiotics. Making using multiscale computer simulations, this project aims at obtaining a deeper understanding of conformational dynamics, enzyme catalysis, as well as the chemomechanical coupling mechanisms under which the chemical free energy is converted into mechanical work in ABC-transporters. | ABC-transporters are responsible for extrusions of various antibiotics. Making using multiscale computer simulations, this project aims at obtaining a deeper understanding of conformational dynamics, enzyme catalysis, as well as the chemomechanical coupling mechanisms under which the chemical free energy is converted into mechanical work in ABC-transporters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == QM/MM development == | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 11 July 2012
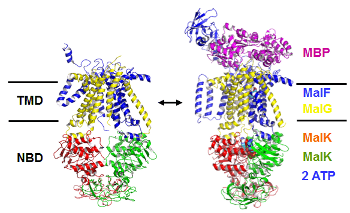
ABC-transporters
Many essential functions of living cells are performed by nanoscale motors consisting of protein complexes. The ability of these biomolecular motors to utilize chemical free energy to perform mechanical work makes them splendid molecular machines. Among various types of molecular motors, ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters represent a unique family of motor proteins that enable translocations of various substrates across cell membranes, by harnessing the free energy associated with ATP binding and hydrolysis. Dysfunctions of ABC-transporters have been linked to a number of diseases, including cystic fibrosis, the most common fatal hereditary disease in the US. The over expressions of certain ABC-transporters are also known to contribute to multidrug resistance of tumor cells after cancer patients receive chemotherapy. In bacterial cells, ABC-transporters are responsible for extrusions of various antibiotics. Making using multiscale computer simulations, this project aims at obtaining a deeper understanding of conformational dynamics, enzyme catalysis, as well as the chemomechanical coupling mechanisms under which the chemical free energy is converted into mechanical work in ABC-transporters.