Difference between revisions of "The Pu Research Group"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (73 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:<span style="display:none"></span>}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:<span style="display:none"></span>}} | ||
| − | [[File:Pu_IUPUI_Banner.jpg|center]] | + | [[File:Pu_IU_Indy_Banner.svg|540px|center|link=http://pu.lab.indianapolis.iu.edu/]] |
| + | <!-- [[File:Pu_IUPUI_Banner.jpg|center|link=http://pu.lab.indianapolis.iu.edu/]] --> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
dynamical motions that are encoded in their three dimensional structures. | dynamical motions that are encoded in their three dimensional structures. | ||
Ongoing projects include computer simulations of ABC-transporters and | Ongoing projects include computer simulations of ABC-transporters and | ||
| − | development of combined quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) methods. | + | damaged DNAs and development of combined quantum mechanical/molecular |
| + | mechanical (QM/MM) methods. | ||
| − | {| cellpadding="2" style="border: | + | {| cellpadding="2" style="border: 0px solid darkgray;" align="center" |
| − | | | + | ! width="250" | |
| − | |- | + | ! width="250" | |
| + | ! width="250" | | ||
| + | |- align="center" | ||
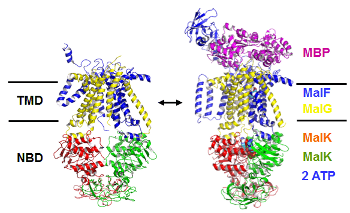
| [[File:MalEFGK2.png|Maltose transporter from ''E. coli''|link=Research]] | | [[File:MalEFGK2.png|Maltose transporter from ''E. coli''|link=Research]] | ||
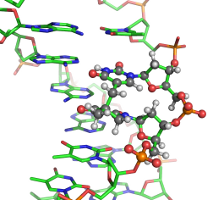
| − | | | + | | [[File:tt_sp.png|SP lesion in DNA|link=Research]] |
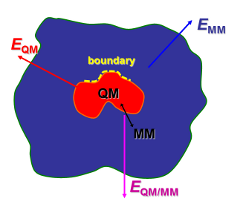
| − | | [[File:qmmm.png|QM/MM]] | + | | [[File:qmmm.png|QM/MM|link=Research]] |
|- align="center" | |- align="center" | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:23, 29 March 2024
Our interests lie at the interface between theoretical/computational chemistry and biophysics. The current research in the lab is directed towards understanding how biomolecules perform their functions via dynamical motions that are encoded in their three dimensional structures. Ongoing projects include computer simulations of ABC-transporters and damaged DNAs and development of combined quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) methods.
|
|
|
